 今年二月,我們團隊順利完成本院第30例小腸移植,她約30歲,是一個慢性小腸偽阻塞症候群的病人,也就是腸蠕動不良的病人,即使用了各種瀉劑,拉了小腸造口,仍無法改善;吐與嗝氣成了她的日常,移植前更常因腸阻塞造成腸炎住院治療。移植後一個月她順利出院,現在可以開始嘗試吃各種食物,讓她很開心,也感謝大愛捐贈。
今年二月,我們團隊順利完成本院第30例小腸移植,她約30歲,是一個慢性小腸偽阻塞症候群的病人,也就是腸蠕動不良的病人,即使用了各種瀉劑,拉了小腸造口,仍無法改善;吐與嗝氣成了她的日常,移植前更常因腸阻塞造成腸炎住院治療。移植後一個月她順利出院,現在可以開始嘗試吃各種食物,讓她很開心,也感謝大愛捐贈。
這些小腸移植後的病人在我們的小腸移植特別門診按月回診,有移植完4-12年的學長姐,有移植完1-3年的學弟妹,每次門診遇到時的吱吱喳喳,也是另類病友會,提供彼此扶持。門診也有其他腸衰竭病友,疾病非常多元,也不是每一個都需要腸移植,也有病患經過腸復健,減少或不須點滴。針對短腸症,我們也有最尖端的GLP-2第二型類升糖胜肽類似物的第三期臨床試驗來改善患者的腸吸收。在小孩,也與內分泌科協同以生長因子輔助腸成長等。在腸衰竭病友的居家靜脈營養,我們除了以原洞更換人工血管大幅減少感染外,也以純魚油輸注避免肝衰竭的發生,照顧的複雜度很高,但我們努力提供這些腸衰竭患者最完整與高品質的治療,也算是另類的精準醫療。
腸衰竭的成因
腸衰竭是一種怎麼樣的疾病,成因基本上分為三類,第一類是短腸症,在成人較常是因為腸中風,在兒童則比較多是因為中腸扭結而切除大量小腸導致腸衰竭;第二類是腸蠕動不良,在成人較多是慢性小腸偽阻塞症候群,表現就是慢慢肚子越來越脹,吐、打嗝、與吃不下食物;第三類是小腸黏膜病變,導致食物無法吸收,在嬰兒可能是小腸黏膜發生病變,表現就是不斷的腹瀉。這些腸衰竭的病人,因為無法從腸道吸收足夠營養,就必須輔以靜脈營養,因為是一件長期的事,因此就會朝向以人工血管做居家靜脈營養進行。
腸衰竭的治療
腸衰竭治療的首重減少靜脈營養的併發症,主要有四項:1.減少人工血管感染:因為一旦感染就是危及生命的敗血症,因此,團隊相當重視管路管理。2.減少輸注營養的大血管栓塞:我們有四處大血管,這些大血管都是他們的命脈,因此,團隊對於這些血管是非常珍視的。3.減少肝臟病變:靜脈營養會導致膽汁鬱積,此外有一些靜脈營養的成份,與腸道的細菌毒素都有一些會肝毒性,慢慢引起肝衰竭,因此,如何適時的調整靜脈營養、給藥、與治療都需要因人制宜。4.代謝性的疾病:這些病人容易因為異常的吸收模式導致腎結石或膽結石,也有人因為維生素缺乏導致骨質酥鬆骨折,或是微量元素不足而貧血或落髮等,團隊也必須適時給予監測與藥物減少併發症。
其次則是提升生活品質與腸道復建,如何讓這些病人在點滴與口慾上達到一種平衡,針對合適的個案進行腸道復健,主要有四項:1. 促進消化吸收的藥物,2.挑選適合的腸道靜脈營養品與給予方式,3. 增進腸絨毛成長與吸收營養品,4.增進腸黏膜生長與吸收的內分泌如第二型類升糖胜類似物 GLP-2或生長因素。GLP-2類似物因為相當昂貴,一個月的藥費就超過百萬,因此目前國內雖有藥証,尚無人使用報告。我們團隊有幸參加一個跨國第三期的GLP-2類似物臨床試驗,可以不用費用使用藥物,相關的結果尚在觀察。總是希望對合適的腸衰竭病人有幫忙。
小腸移植
腸衰竭的病人都希望有朝一日能回到跟正常人一樣吃的日子,小腸移植就是這些病人最後一線的希望,團隊針對符合腸移植適應症的病人列入腸移植的名單,一年365天隨時待命,在大愛降臨時展開即刻救援,從取器官到種器官與術後的照顧,有賴許多醫療團隊一起奮鬥。因為腸道的免疫系統很強,移植後半年很容易發生急性排斥與伺機性感染,等順利出院後需要半年的縝密觀察期,在小心照顧下約半年一年後可以關閉監測用的迴腸照口,移除人工血管,過著跟正常人一樣的生活。
當然,門診時我也會認真看每個指標,決定是不是要調降抗排斥藥物的濃度,減少抗排斥藥物所帶來的各種併發症,以及各種用藥的調整。到現在,不計入臨床試驗前期的話,能夠有五年75%的病人整體存活率,是相當不錯的成績。
困境與挑戰:活體小腸移植
從2007年開始執行第一例小腸移植到現在30例,團隊遇到的挑戰很多,醫療上的問題,例如排斥與感染等,我們一一建置SOP,能好好處理。由於兒童族群的腸衰竭需要體型相符的捐贈者,不容易等到大愛捐贈,發生好多起等候中死亡的憾事,我們因此努力完成活體小腸移植的動物實驗,並通過活體小腸移植的臨床試驗,希望能幫忙這些等不到器官、危急的病人族群,抑或是國外腸衰竭的個案,可以藉由親屬捐贈進行活體小腸移植。
院長室/小兒外科 陳芸副院長
專長:小兒疝氣、隱睪症、包皮炎、小兒腸胃道與肝膽方面手術、小兒胸廓畸型、漏斗胸、雞胸、小兒泌尿系統相關手術、新生兒先天性畸型之重建手術、舌繫帶、皮下腫瘤、斜頸等門診小手術、小腸移植與腸衰竭重建
https://www.femh.org.tw/section/sectionDetail2?CID=0289&&DoctorID=81138

小腸移植30例的新里程碑
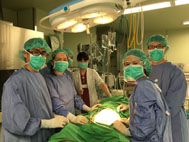
本院小腸移植團隊予今年2月完成第30例
A new milestone in 30 cases of small intestine transplantation-talk about the care of patients with intestinal failure
In February this year, our team successfully completed the 30th case of small bowel transplantation in our hospital. She is about 30 years old and is a patient with chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction syndrome, that is, a patient with poor bowel peristalsis. She can’t eat well; vomiting and burping became her daily routine, and she was often hospitalized for enteritis due to intestinal obstruction before transplantation. One month after the intestinal transplant, she was successfully discharged from the hospital, and now she can start to try various foods, which makes her very happy, and thanks the one who donate bowel. These patients after small bowel transplantation return to our special outpatient clinic on a monthly basis. Some of them have been transplanted for 4-12 years, and some of them have been transplanted for 1-3 years. Every time they meet at our outpatient clinic, they will squeak and chatter. It is also an alternative patient association, providing mutual support. There are also other patients with intestinal failure in the outpatient clinic. The etiology of intestinal failure is very diverse, and not everyone needs intestinal transplantation. For short bowel disease, we also have the most cutting-edge Phase III clinical trials of GLP-2 analogs to improve intestinal absorption. In children, it also supports intestinal growth with growth hormone in cooperation with endocrinologist. In the home parental nutrition patients, catheter management is important to prevent infection, we also use pure fish oil infusion to avoid the occurrence of liver failure. The care complexity is high, but we strive to provide these patients with the most complete and high-quality treatment.
Causes of intestinal failure
Intestinal failure is a kind of disease. The causes are basically divided into three categories. The first category is short bowel syndrome. In adults, it is more often due to ischemic bowel disease; the second category is bowel dysmotility, which is mostly chronic small intestinal pseudo-obstruction syndrome in adults, which is characterized by gradually increasing abdominal distension, vomiting, hiccups, and inability to eat food; the third category is intestinal mucosal dysplasia, which lead to food malabsorption, in infants, the mucosa of the small intestine may be dysplasia, and the presentation is intractable diarrhea. These patients with intestinal failure, because they cannot absorb enough nutrients from the intestines, must be supplemented with intravenous nutrition. Furthermore, it is a long-term thing, they will turn to home parenteral nutrition program.
Treatment of intestinal failure
The priority in the treatment of intestinal failure is to reduce the complications of parenteral nutrition. There are four main items: 1. Reduce artificial blood vessel catheter-related infection: once infection, it is life-threatening sepsis, so the team put great effort to prevent catheter infection; 2. Reduce the risk of major veins thrombosis: We have four large blood vessels for infusion parenteral nutrition, so the team is very cherished for these blood vessels to prevent thrombosis. 3. Reduce liver cirrhosis and liver failure: parenteral nutrition can lead to liver cholestasis. In addition, there are some components of parenteral nutrition, and some bacterial toxins in the intestinal tract can cause liver toxicity and progress to cirrhosis and liver failure. Therefore, how to adjust parenteral nutrition and provide treatments need to be tailored individually. 4. Metabolic diseases: These patients are prone to kidney stones or gallstones due to abnormal absorption patterns. Others are prone to osteoporosis and fractures due to vitamin deficiency, or anemia or hair loss due to insufficient trace elements. The team must also provide timely monitoring and give medications to reduce complications. The second is to improve the quality of life and intestinal rehabilitation. How to make these patients achieve a balance between PN and oral intake, and intestinal rehabilitation for suitable cases, there are mainly four: 1. Drugs to promote digestion and absorption, 2. Choose the appropriate enteral nutrition and delivery method, 3. Enhance intestinal villus growth by nutrients such as glutamine, 4. Enhance intestinal mucosal growth and absorption by endocrine such as GLP-2 or GLP-2 analogs. Because commercial GLP-2 analogues are quite expensive, the monthly drug cost exceeds one million NTD currently. Therefore, no one has reported their use in Taiwan. Our team is fortunate to participate in a multinational Phase III clinical trial of GLP-2 analogs, and the drug can be used at no cost, and the relevant results are still under observation. We always hope to help these bowel failure patients in every direction.
Intestinal transplantation
Patients with intestinal failure hope that one day they can return to eating like normal people. Small intestine transplantation is the last hope for these patients. The patients who meet the indications for intestinal transplantation is on the waiting list and the team is on call 365 days a year, to carry out immediate organ transplantation when brain-death donor comes. Because the intestinal immune system is very strong, acute rejection and opportunistic infection are easy to occur six months within transplantation. After a successful discharge from the hospital, a careful observation period of six months is required. After that, the ileostomy for rejection monitoring can be closed, remove the artificial blood vessels catheter, and live a normal life. Of course, at the outpatient clinic, we will carefully look at each parameter and adjust immunosuppression drugs. So far, excluding the pre-clinical trial period, the overall 5-year patient survival rate is 75% , which is good and comparable with other big centers in USand EU.
Dilemmas and challenges: Living donor intestinaltransplantation
Since the first small bowel transplantation in 2007, we have now performed 30 cases. The team has encountered many challenges, medical problems, such as rejection and infection, we have established SOPs one by one and can handle them well now. Because the intestinal failure of the children needs a size match donor,it is not easy to wait for the brain-death donor, and there are many regrets of dying while waiting. Therefore, we strive to complete the animal experiment of living-donor intestinal transplantation and approve the clinical trial of living-donor intestinal transplantation by MOH. Hope the trial can help these patients who cannot wait for organs, critical patient groups, or cases of intestinal failure abroad, and part of the intestine can be donated by relatives for living-donor intestinal transplantation.