Specialties: Minimally invasive kidney and ureteral stone treatment (extracorporeal shock wave therapy, flexible ureteroscopy), urinary dysfunction assessment and treatment (medication, electrosurgical curettage, laser vaporization, hydrovapor ablation, prostate lift), hernia treatment and urinary system reconstruction (Da Vinci hernia repair, traditional circumcision, circumcision gun, single-port ligation)
Uncle Wang recently chatted with his
neighbor, Uncle Li, and discovered that although both had undergone inguinal
hernia surgery, their expenses were vastly different. Uncle Wang received the traditional
hernia repair covered by national health insurance, with almost all costs paid
by insurance. Uncle Li, on the other hand, chose the latest Da Vinci
robotic-assisted surgery and had to pay as much as NT$160,000 out of pocket!
(To be continued...)
What Is an Inguinal Hernia?
An inguinal hernia, commonly known as a
"rupture," occurs when an organ inside the abdominal cavity
abnormally protrudes through a hole in the abdominal wall muscles or fascia.
The inguinal region is where the abdomen meets the thigh and is the weakest
part of the abdominal wall. In men, the spermatic cord passes through here; in
women, the round ligament of the uterus passes through.
Causes of Hernia
The main cause is the weakening or
defect of the abdominal wall muscles and fascia, due to injury, aging, or
congenital defects. Factors that increase abdominal pressure and lead to
hernias include:
- Obesity
- Prolonged standing or sudden heavy lifting
- Long-term heavy work
- Chronic prostate enlargement causing straining
during urination
- Chronic constipation
- Persistent coughing or
sneezing
Symptoms of Hernia
About 95% of hernias are visible
externally. Main symptoms include:
- A bulging sensation,
dull pain, or a noticeable lump in the groin
- More apparent when standing or straining the
abdomen
- The bulge disappears when lying down
- Burning, pain, or swelling at the protrusion
- Occasional pulling pain
or heaviness in the groin, especially when bending, coughing, or lifting
**If you experience sudden severe pain,
be cautious of a strangulated hernia and seek immediate medical attention.
Comparison of Hernia Surgery Methods
|
Surgery Type
|
Traditional Open Surgery
|
Laparoscopic Hernia Repair
|
Da Vinci Robotic Surgery
|
|
Wound Size/Appearance
|
Larger wound (5-8 cm), obvious scar
|
Small wounds (three 0.5-1 cm holes),
small scars
|
Extremely small wounds, best
appearance
|
|
Pain
|
More obvious
|
Milder, less postoperative pain
|
Minimal, least postoperative
discomfort
|
|
Recurrence Rate
|
~4-15%
|
~3-10% (varies by surgeon experience)
|
~3-5%
|
|
Recovery Speed
|
Longer (10-21 days for daily
activities)
|
Fast (6-14 days for daily activities)
|
Fast (similar to laparoscopy)
|
|
Hospital Stay
|
Longer (1-2 days or more)
|
Shorter (most can be discharged same
day)
|
Shorter (most can be discharged same
day)
|
|
Anesthesia
|
Local, spinal, or general
|
General anesthesia
|
General anesthesia
|
|
Infection Risk
|
Higher (large wound)
|
Lower (small wound)
|
Lowest
|
|
Complications
|
Nerve injury, bleeding, infection,
chronic pain
|
Organ injury, hematoma, emphysema,
chronic pain
|
Low complication rate, rare bleeding
or infection
|
|
Suitable For
|
Almost all hernias, especially
large/complex
|
Bilateral, recurrent, younger patients
|
Precision needs, complex or recurrent
hernias
|
|
Disadvantages
|
Large wound, slow recovery, more pain,
higher infection rate
|
Requires general anesthesia, steep
learning curve, higher cost, not suitable for all hernias
|
Highest cost, longer surgery, high
equipment/training needs
|
|
Cost
|
Lower
|
Higher
|
Highest
|
|
Surgeon Experience Impact
|
Less, highly standardized
|
High, inexperience increases recurrence
|
Requires high training, experience
matters greatly
|
Postoperative Care Tips
Wound Care
- Keep the wound clean and dry
- Apply ice packs to the
groin or scrotum area on the first day after surgery
- Watch for redness, swelling, heat, or pain at the wound
Activity Restrictions (First 3 Months)
- Avoid constipation or straining during bowel movements
- Avoid bending to lift
heavy objects (over 5 kg)
- Avoid vigorous exercise
like running or playing ball
- Avoid sit-ups, push-ups
- Avoid cycling or riding
a motorcycle
- Avoid sexual activity (recommended to wait one month)
Dietary Recommendations
- Eat more high-fiber foods, vegetables, and fruits to prevent
constipation
- Eat more high-protein
foods (milk, eggs, fish, meat) to promote wound healing
- Drink plenty of water (2000-3000 c.c. per day)
Why the Cost Difference?
After discussing, both realized that the
cost difference comes not only from the surgical method but also from many
details. For example, there are basic mesh implants covered by insurance and
premium self-pay meshes with different materials and comfort levels. There are
also optional self-pay items like hemostatic powders, gels, and products that
promote wound healing to improve surgical quality and speed up recovery. The
need for these depends on the complexity of the hernia, individual health, and
expectations for recovery.
Therefore, both Uncle Wang and Uncle Li
agree that the choice of surgical method is not just about cost. It should be
based on your physical condition, the severity of the hernia, and thorough
discussion with your doctor to choose the most suitable treatment. Necessary
medical materials and self-pay items should be decided according to personal
needs and professional medical advice, to balance safety, effectiveness, and
financial burden.
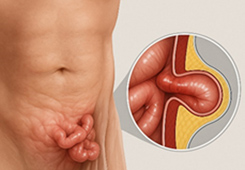
Diagram of an inguinal hernia